Understanding Data Broker Privacy Policies – Key Insights for Protecting Your Personal Information
In the digital age, the collection and management of personal information have become integral to the functioning of various online services. This section delves into the complex world of entities that gather and sell such details, exploring the nuances of their operational frameworks. By examining the practices of these information aggregators, we aim to shed light on the implications for individual rights and the broader digital ecosystem.
Key Aspects of Information Handling
Information aggregators operate within a framework that often involves the compilation of vast amounts of personal data. This data is then made available to interested parties, typically for commercial purposes. The transparency and fairness of these transactions are critical, yet they often remain opaque to the average consumer. Understanding the mechanisms through which these entities manage and protect the information they collect is essential for safeguarding personal privacy in the digital realm.
Navigating the Legal and Ethical Terrain
As we navigate through this intricate landscape, it becomes apparent that the legal and ethical considerations surrounding information aggregation are multifaceted. Regulations and ethical guidelines play a pivotal role in shaping the behavior of these entities. However, the effectiveness of these frameworks can vary significantly, influenced by technological advancements and the evolving nature of online interactions. This section will provide insights into how these challenges are addressed and what steps can be taken to enhance the protection of personal information.
Understanding Data Brokers
This section delves into the concept of entities that aggregate and manage vast amounts of personal information. These organizations play a crucial role in the digital economy, often operating behind the scenes.
Who Are These Entities?
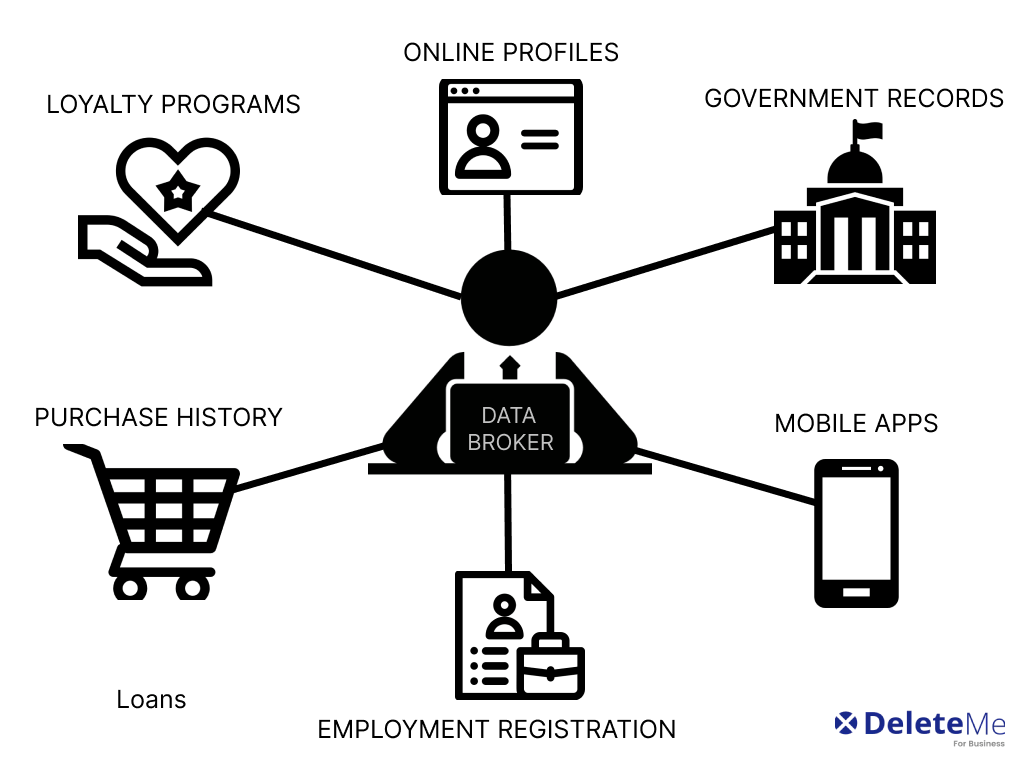
These entities are companies that collect, analyze, and sell personal details to other businesses. They gather information from various sources, including public records, online activities, and other commercial transactions. The primary goal of these entities is to provide comprehensive profiles that can be used for marketing, research, and other commercial purposes.
Operational Scope
Their operations span across multiple industries, influencing everything from targeted advertising to credit scoring. By consolidating diverse data sets, these entities enable businesses to make informed decisions based on detailed consumer profiles.
Regulatory Landscape
The activities of these entities are subject to various regulations aimed at ensuring the ethical use of personal information. Understanding the legal framework that governs these operations is essential for both consumers and businesses.
Consumer Impact
For consumers, the presence of these entities means that personal information is constantly being collected and analyzed. This can have significant implications for privacy and the way individuals are perceived by potential employers, insurers, and marketers.
In summary, these entities are pivotal in the modern data-driven economy, influencing numerous aspects of daily life. Their role, however, necessitates a careful balance between utility and privacy concerns.
Who Are Data Brokers?
This section delves into the entities that gather and sell personal information, often operating behind the scenes. These organizations play a significant role in the digital economy, yet their operations are not always transparent to consumers.
These entities collect a wide array of personal details, ranging from basic contact information to more sensitive data like purchasing habits and online behavior. The methods they employ to gather this information are diverse and can include both legal and ethically questionable practices.
- Public Records: Many of these organizations start by compiling publicly available information, such as property records, court documents, and professional licenses.
- Online Tracking: Through cookies and other tracking technologies, they monitor internet activity to build profiles of individuals’ online behaviors and preferences.
- Third-Party Sources: They often purchase data from other companies, including retailers, credit agencies, and social media platforms.
- Surveys and Promotions: Participation in surveys, contests, and promotional offers can also lead to the collection of personal data.
The information collected is then packaged and sold to businesses, marketers, and sometimes even government agencies. This practice allows these entities to target advertising more effectively, tailor marketing strategies, and even influence consumer behavior. However, it also raises significant concerns about consent and the right to privacy.
Understanding how these organizations operate is crucial for consumers to make informed decisions about their online activities and to protect their personal information effectively.
How Data Brokers Collect Information

Information Gathering Techniques: This section delves into the various methods employed by entities that aggregate and sell personal details. Understanding these practices is crucial for consumers to grasp the breadth of their digital footprint.
Direct Collection: One of the primary ways these entities gather details is through direct interactions. This includes purchasing lists from various sources, such as public records, marketing surveys, and other similar databases. These lists often contain sensitive personal information like names, addresses, phone numbers, and sometimes even financial details.
Online Tracking: Another significant method involves tracking individuals’ online activities. Through the use of cookies, web beacons, and other tracking technologies, these entities can monitor browsing habits, purchase histories, and even social media interactions. This data is then aggregated and analyzed to create detailed profiles of individuals, which are used for targeted advertising and other purposes.
Third-Party Sharing: Many companies share customer information with these entities. This can happen through partnerships, data sharing agreements, or even data breaches. Once shared, this information is combined with other data sets to create comprehensive profiles that can be sold to interested parties.
Public Records and Open Sources: Publicly available information is another rich source of data. This includes information from government records, such as property deeds, court records, and professional licenses. Additionally, open sources like social media platforms, blogs, and forums provide a wealth of personal information that can be collected and utilized.
Surveys and Promotions: Participating in online surveys, contests, and promotions can also lead to information collection. Often, the fine print of these activities includes clauses that allow the organizers to share participants’ details with third parties, including these entities.
Understanding these collection methods is essential for individuals to make informed decisions about their online activities and to take steps to protect their personal information.
Types of Data Collected by Brokers
Overview of Information Gathering: This section delves into the various categories of information that are routinely gathered by entities involved in the consolidation and trade of personal details. These entities, often operating behind the scenes, collect a wide array of data points that can range from the mundane to the highly sensitive. Understanding the nature of this information is crucial for individuals seeking to manage their digital footprint effectively.
Personal Identifiers: One of the primary types of information collected includes personal identifiers such as names, addresses, email addresses, and phone numbers. These details are fundamental for establishing the identity of individuals and are often the starting point for more extensive profiles.
Demographic Details: Brokers also gather demographic information, which includes age, gender, race, and marital status. This type of data helps in creating a more nuanced picture of the target audience, enabling tailored marketing strategies and product offerings.
Financial Information: Sensitive financial details such as credit scores, income levels, and transaction histories are also commonly collected. This information is particularly valuable for financial institutions and companies offering credit-related services.
Online Activity: The digital traces left by individuals on the internet, including browsing history, purchase records, and social media interactions, are meticulously tracked. This data is instrumental in predicting consumer behavior and preferences.
Location Data: With the proliferation of mobile devices, location data has become a significant category. This information can reveal patterns of movement and habits, which are useful for targeted advertising and service provision.
Health Information: In some cases, health-related data, such as medical conditions, prescriptions, and insurance details, are also collected. This category of information is highly sensitive and regulated, but it can be extremely valuable for healthcare-related services.
Understanding the breadth and depth of information collected by these entities is essential for consumers to make informed decisions about their online presence and to advocate for better data protection measures.
Privacy Policy Analysis
Analyzing the policies of information aggregators is crucial for understanding How to opt out of BlockShopper they manage and safeguard personal details. This section delves into the specifics of these policies, examining their transparency, comprehensiveness, and alignment with legal standards.
When assessing these policies, it’s important to consider several key elements. Firstly, the clarity with which they communicate their practices regarding the collection, use, and sharing of personal information. Secondly, the extent to which these policies provide options for individuals to control their information, including the ability to opt-out or modify shared details.
Transparency is a critical factor in this analysis. A policy that clearly outlines what information is collected, why it is collected, and how it is used, enhances trust and allows individuals to make informed decisions about their interactions with information aggregators.
Additionally, the alignment of these policies with relevant laws and regulations cannot be overstated. Compliance with standards set by governing bodies ensures that the rights and interests of individuals are protected, and that the aggregators themselves operate within legal boundaries.
In summary, a thorough analysis of information aggregator policies not only sheds light on their operational methods but also empowers individuals by providing them with the necessary insights to protect their personal information effectively.
Your Rights Regarding Data Brokers
This section delves into the legal protections and rights individuals possess concerning the collection and use of their personal information by entities that aggregate and sell such information. Understanding these rights is crucial for safeguarding one’s personal data in the digital age.
Individuals have several key rights that they can exercise to manage their personal information held by these entities. These rights are often enshrined in various data protection laws and regulations worldwide.
| Right | Description |
|---|---|
| Right to Access | Individuals can request to see what information these entities hold about them. |
| Right to Rectification | Individuals have the right to correct inaccurate or incomplete information about themselves. |
| Right to Erasure | Also known as the right to be forgotten, this allows individuals to request the deletion of their personal data under certain conditions. |
| Right to Object | Individuals can object to the processing of their personal data, especially for marketing purposes. |
| Right to Data Portability | Individuals can obtain and reuse their personal data across different services. |
It is important for individuals to be aware of these rights and to understand how to exercise them effectively. Many countries have established regulatory bodies and mechanisms to help individuals enforce these rights. Engaging with these resources can significantly enhance personal data security and control.
Protecting Your Data Privacy
In this section, we delve into strategies and practices that individuals can employ to safeguard their personal information from unauthorized access and misuse. With the increasing prevalence of digital information collection and storage, it is crucial to understand how to maintain control over one’s own data.
Awareness and Education
The first step in protecting personal information is to stay informed about current practices and technologies that affect data security. This includes understanding the types of information that are commonly collected and the methods used to gather this data. By educating oneself, individuals can better recognize potential risks and take appropriate measures to mitigate them.
Use of Strong, Unique Passwords
Creating and using strong, unique passwords for each online account is a fundamental practice in data protection. Passwords should be complex, combining letters, numbers, and special characters, and should not be reused across different platforms. Utilizing a password manager can also enhance security by generating and storing strong passwords securely.
Regular Software Updates
Keeping all software, including operating systems and applications, up to date is essential. Updates often include patches for security vulnerabilities that could be exploited by malicious actors. Setting automatic updates where possible ensures that systems are protected as soon as new patches are available.
Use of Encryption
Encrypting sensitive data, both at rest and in transit, adds an additional layer of security. Encryption transforms data into a format that can only be read by those with the correct decryption key. This practice is particularly important for protecting information stored on devices or transmitted over networks.
Limit Sharing of Personal Information
Minimizing the amount of personal information shared online can significantly reduce the risk of data breaches. Individuals should be cautious about the details they provide on social media platforms and other websites, and should regularly review and adjust privacy settings to control who has access to their information.
Regular Monitoring and Review
Regularly monitoring accounts for any unusual activity can help detect potential breaches early. Reviewing privacy settings and the types of information collected by various services is also important to ensure that data practices align with personal preferences and security standards.
By implementing these strategies, individuals can take proactive steps to protect their personal information in an increasingly digital world. It is crucial to remain vigilant and adapt to new security challenges as they arise.
Future of Data Broker Regulation
As the digital landscape evolves, so too must the frameworks governing the collection and utilization of personal information. This section delves into the emerging trends and potential reforms that could reshape the regulatory environment for entities that aggregate and trade user data.
Technological advancements and increasing public awareness have spurred a critical examination of current practices. The future regulatory framework is likely to be characterized by more stringent requirements for transparency and consent. Legislators and policymakers are increasingly recognizing the necessity for comprehensive regulations that protect individual rights while fostering a balanced digital economy.
One of the key areas under scrutiny is the standardization of data collection methods. Future regulations may mandate clearer disclosure of what information is being gathered, how it is used, and with whom it is shared. This could involve setting stricter guidelines for anonymization techniques to ensure that personal identifiers are effectively removed.
Additionally, there is a growing movement towards data minimization, where regulations could limit the amount of information collected to only what is necessary for a specific purpose. This approach not only enhances privacy but also reduces the risk of data breaches and misuse.
Another significant trend is the integration of AI and machine learning into regulatory compliance. Advanced algorithms could be employed to monitor and audit data practices, ensuring adherence to new standards in real-time. This technological synergy could also aid in the detection and prevention of unauthorized data transfers and sales.
The role of international cooperation in shaping future regulations cannot be overstated. As data flows transcend national boundaries, harmonized international standards will be crucial. This global approach will help in creating a consistent level of protection for individuals regardless of their geographic location.
In conclusion, the future of regulation in this domain is poised to be more dynamic and responsive to technological changes and public demands. By embracing these emerging trends, the regulatory framework can effectively safeguard individual privacy while supporting innovation and economic growth in the digital era.



